Welcome to the Anticoagulation Reversal Learning Center
In The News
ANDEXXA Phase IV Trial Stopped Early after Achieving Criteria on Hemostatic Efficacy
ANNEXA-I, a post-marketing Phase IV trial to assess the efficacy and safety of Andexxa (andexanet alfa) in patients on oral FXa inhibitor treatment experiencing an intracranial hemorrhage will be stopped early, AstraZeneca, t
Read moreLatest Research
Fixed-dose four-factor PCC for the reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitor-associated bleeding
Four-Factor PCC (4F-PCC) is labeled for the reversal of vitamin K antagonists and may be considered off label for the reversal of factor Xa inhibitors. A fixed-dose strategy of 4F-PCC for the reversal of factor Xa inhibitors has the potential to minimize delay to reversal, avoid confusion during the ordering process, and lead to cost savings.
Read more
Management of major bleeding for anticoagulated patients in the Emergency Department: an European experts consensus statement
An increasing number of patients presenting to the emergency department (ED) with life-threatening bleeding are using oral anticoagulants, such as warfarin, Factor IIa and Factor Xa inhibitors. Achieving rapid and controlled haemostasis is critically important to save the patient’s life. This multidisciplinary consensus paper provides a systematic and pragmatic approach to the management of anticoagulated patients with severe bleeding at the ED.
Read more
Perioperative Considerations in Management of the Severely Bleeding Coagulopathic Patient
Inherited and acquired coagulopathy are frequently associated with major bleeding in severe trauma, cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass, and postpartum hemorrhage. Perioperative management is multifactorial and includes preoperative optimization and discontinuation of anticoagulants and antiplatelet therapy in elective procedures.
Read more
Full Reversal of Anticoagulants Before Cephalomedullary Fixation of Geriatric Hip Fractures May Not Be Necessary
To examine the relationship between anticoagulant and antiplatelet drugs and surgical blood loss for geriatric patients undergoing cephalomedullary nail fixation of extracapsular proximal femur fractures.
Read more
Andexanet alfa vs. four-factor prothrombin complex concentrate
Andexanet alfa (Andexxa, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals) is a specific factor Xa reversal agent approved for life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding associated with the factor Xa inhibitors, apixaban (Eliquis) and rivaroxaban (Xarelto).
Read more
Final Study Report of Andexanet Alfa for Major Bleeding With Factor Xa Inhibitors
Conclusions: In patients with major bleeding associated with the use of FXa inhibitors, treatment with andexanet alfa reduced anti-FXa activity and was associated with good or excellent hemostatic efficacy in 80% of patients.
Read more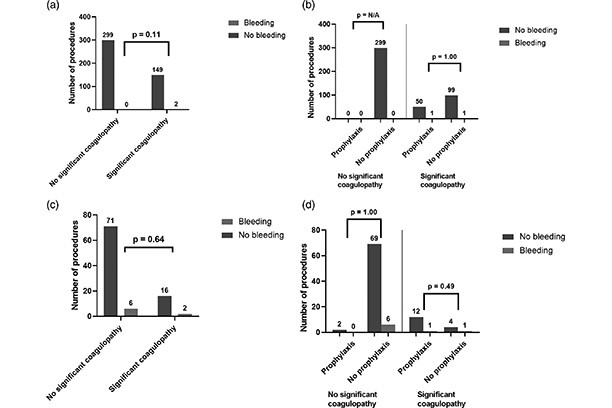
Procedural bleeding risk, rather than conventional coagulation tests, predicts procedure related bleeding in cirrhosis
Procedure-related bleeding in cirrhotic patients cannot be accurately predicted by INR or platelet count, nor prevented by blood component prophylaxis using these parameters. Procedure-related bleeding is best predicted by the bleeding risk status of procedures.
Read moreCase Studies
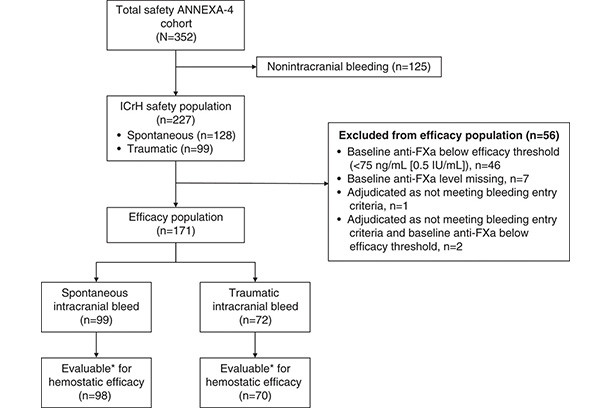
Hemostatic Efficacy and Anti-FXa (Factor Xa) Reversal With Andexanet Alfa in Intracranial Hemorrhage: ANNEXA-4 Substudy
Andexanet alfa is a recombinant modified human FXa (factor Xa) developed to reverse FXa inhibition from anticoagulants. Hemostatic efficacy and reversal of anti-FXa activity with andexanet were assessed in patients from the ANNEXA-4 study (Andexanet Alfa, a Novel Antidote to the Anticoagulation Effects of FXa Inhibitors) with intracranial hemorrhage (ICrH).
Read more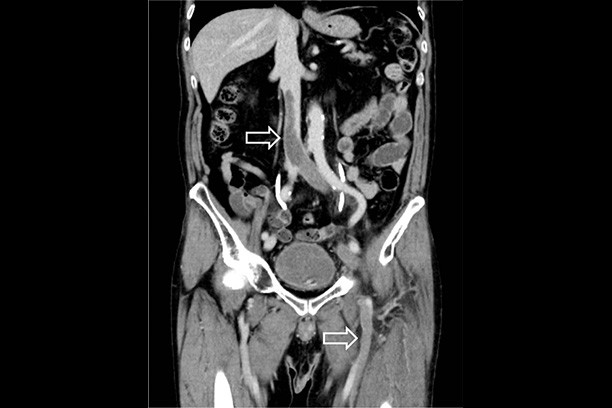
Effect of combined therapy with catheter-directed thrombolysis and factor Xa inhibitor for inferior vena cava thrombosis
Inferior vena cava (IVC) thrombosis is an under-recognized entity that is associated with a mortality rate approaching twice that of lower extremity deep venous thrombosis (DVT). Thrombolytic therapy not only results in greater lysis, but also results in higher complication rates than anticoagulation alone.
Read more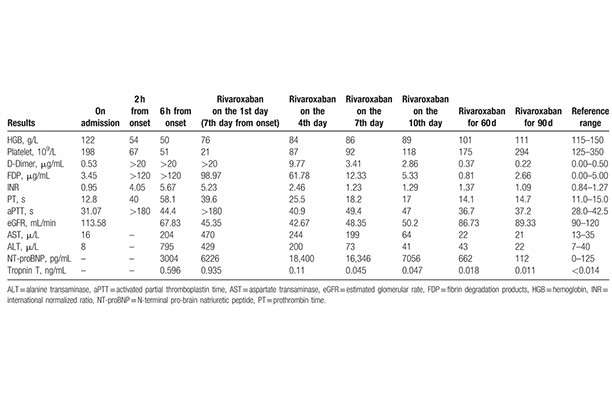
Successful treatment of amniotic fluid embolism complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulation with rivaroxaban
An amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is a rare, lethal syndrome that is commonly associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Anticoagulation therapy is the most important strategy to inhibit excessive activation of the coagulation cascade in patients with AFE and DIC. At present, treatment of AFE with rivaroxaban has not been reported.
Read more